Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Remote Sensing for Geographical Information Systems (GIS)
Remote Sensing Applications in the modern world
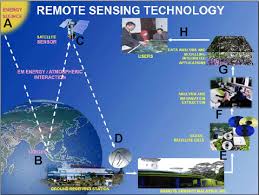
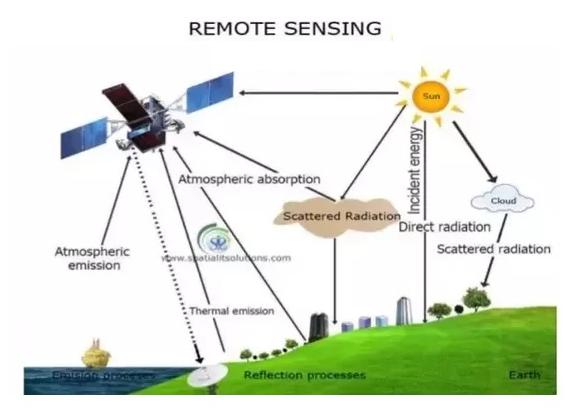
Remote sensing is the process of detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance from the targeted area. Special cameras collect remotely sensed images of the Earth, which help researchers "sense" things about the Earth.
Remote sensors collect data by detecting the energy that is reflected from Earth. These sensors can be on satellites or mounted on aircraft.
Remote sensors can be either passive or active. Passive sensors respond to external stimuli. They record natural energy that is reflected or emitted from the Earth's surface. The most common source of radiation detected by passive sensors is reflected sunlight.
In contrast, active sensors use internal stimuli to collect data about Earth. For example, a laser-beam remote sensing system projects a laser onto the surface of Earth and measures the time that it takes for the laser to reflect back to its sensor.
From a general perspective, remote sensing is the science of acquiring and analyzing information about objects or phenomena from a distance. As humans, we are intimately familiar with remote sensing in that we rely on visual perception to provide us with much of the information about our surroundings.