Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Fascism: Introduction, History, Characteristics, Principles, Description

What does Fascism mean? What is the ideology of Fascism? Definition and Facts
Fascism is a radical authoritarian political ideology. Fascists seek rejuvenation of their country on the basis of commitment to an organic national community. Under Fascism, its individuals are united together in the national identity as one people by suprapersonal connections of culture, ancestry, and blood through a totalitarian single-party state.
A Fascist state demands the mass mobilization of a nation through indoctrination, discipline, introduction, physical education, and eugenics. Fascism wants to purify the country of foreign influences that are deemed to be causing degeneration of the country or of not fitting into the national culture. Fascism promotes political violence and war, as forms of direct action that create national regeneration, emotions, and vitality.
Fascists usually use paramilitary organizations for the violence against the opponents or overthrow the political system. Fascism opposes many ideologies: conservatism, liberalism, and two major forms of socialism-communism and social democracy.
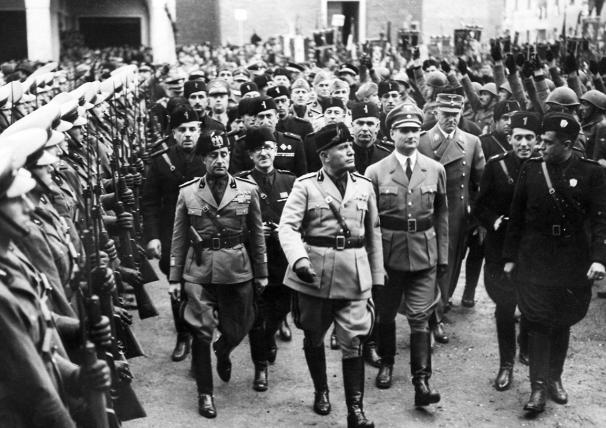
In 1919, Benito Mussolini described fascism as a syncretic movement that would strike "against the backwardness of the right and the destructiveness of the left". Italian Fascists described fascism as a right-wing ideology in the political program The Theory of Fascism: "We are free to believe that this is the century of authority, a century tending to the 'right,' a fascist century."