Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Space Rocket: PSLV and GSLV Feature and Specification
Space: Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) Feature and Specification
When we use a rocket to launch anything to orbit the part that goes into orbit is the payload and the part that does not is the launch vehicle.
Sometimes parts of the launch vehicle are traveling so rapidly they also end up in orbit, but most of these do not stay in orbit, and they normally have no useful function once they separate from the payload.
For the American Space Shuttle for example when the Shuttle (payload) is going fast enough to orbit it aims slightly downward before releasing the External Tank, then maneuvers back up slightly using the OMS.
This was done so that the External Tank would go low enough to deorbit quickly from friction with the upper atmosphere instead of staying in orbit for days or weeks along with the Shuttle itself.
Some launch systems include deorbiting fuel for the same reason, to remove the upper stage from orbit as quickly as possible instead of letting it slowly decay and fall at some random location.
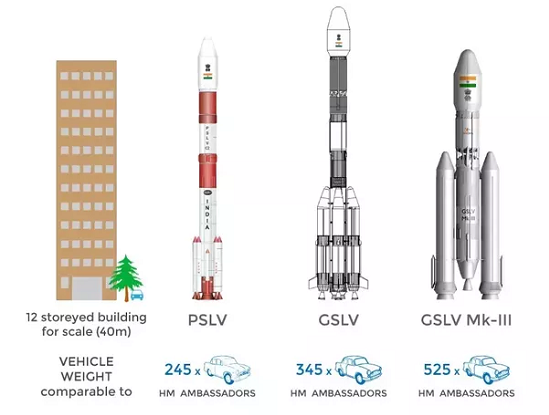
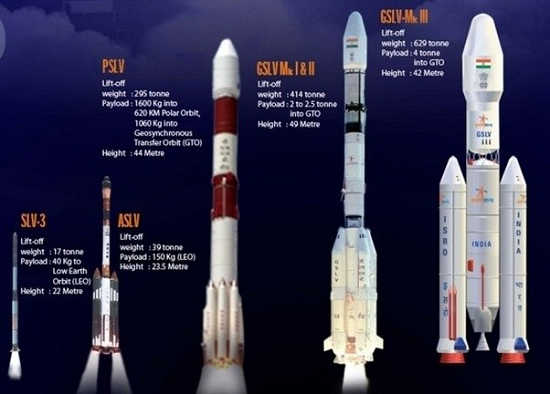
ISRO use two types of launch vehicles viz. the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV).
The PSLV has four stages using solid and liquid propulsion systems alternately whereas the GSLV is a three-stage vehicle with solid, liquid and cryogenic stages respectively.