Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Constitution: Parliamentary System and Amendment Procedures

Constitution: Indian Parliamentary System and Amending the Constitution Of India and Part XX (Article 368)
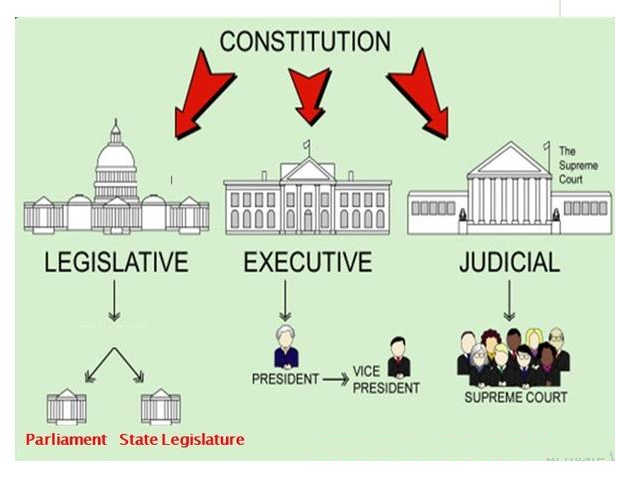
Parliamentary System:
The Constituent Assembly decided to support the Parliamentary form of government for both Centre and the states. A parliamentary system is a system of democratic governance of a state where the executive branch receives its democratic legitimacy from the legislature and is also held responsible for the legislature. In a parliamentary system, the head of state is usually a separate person from the head of government.
In the Indian parliamentary system, there is a distinction between nominal and actual executive heads. The Council of Ministers is responsible before the Lok Sabha, The lower house of union parliament.
Amending the Constitution of India:
Amending the Constitution of India is the procedure of making modifications the fundamental law of the country or supreme law. The procedure of amendment in the constitution is to determined in Part XX (Article 368) of the Constitution of India. This process guarantees the sanctity of the Constitution of India and keeps a check on the uninformed power of the Parliament of India.
When comparing the other countries' constitution, the constitution of India provides a specific amendment process. It can be defined as partially flexible and partially rigid. The Constitution provides for a variety in the amending process.