Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Optical Fibre (Optical Fiber) Features, Properties, Types
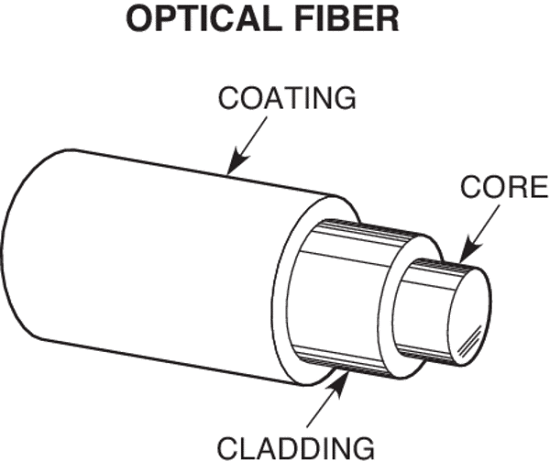
Electronics: Optical Fibre Definition, Low loss, wideband, lightweight and Non-inductive Properties
Optical fibre refers to the medium and the technology associated with the transmission of information as light pulses along a glass or plastic strand or fibre.
A fibre optic cable can contain a varying number of these glass fibres -- from a few up to a couple hundred. Surrounding the glass fibre core is another glass layer called cladding.
(1) Low loss
Optical fibre features low loss compared either to the metallic, balanced paired cable or coaxial cable using copper.
(2) wideband
The optical fibre can transmit signals at far higher frequencies than coaxial cable, although the frequency range depends on the fibre type.
(3) The short diameter and lightweight
it is narrower and lighter than other transmission media. Compared to 18-core coaxial cable, for example, the 18-core optical cable is about 1/10 in sectional area and about 1/30 in weight. Optical cable,
(4) Non-inductive
Since glass such as quartz does not conduct electricity, the optical fibre is free of noise resulting from electromagnetic induction from external objects (such as high-tension cables, TV sets, and radios).


