Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
MCR-1 Gene History, Discovery, Superbug behavior, Features, Threat to Humanity
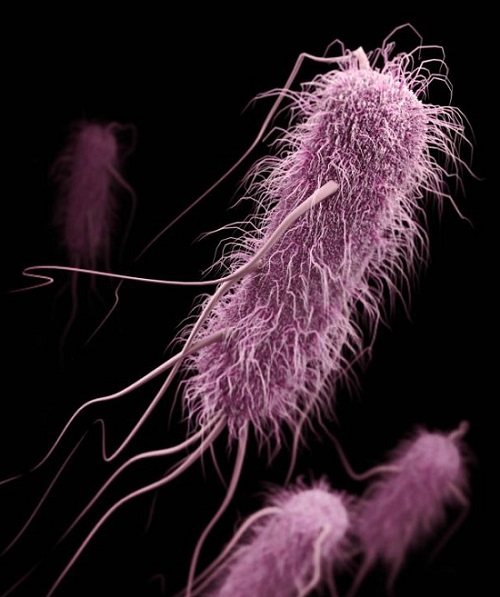
MCR-1 Gene a pan-drug resistant gene discovered in India, Mechanism, Superbug, Colistin
Indian researchers have isolated a strain of E.Coli bacteria, carrying a new gene (mcr -1), described previously as truly pan-drug resistant’ It is resistant to the last mile antibiotic the human race currently has access to - colistin.
The MCR-1 is a genetic mechanism by which the mcr-1 gene confers the first known plasmid-mediated resistance to colistin, a polymixin and one of a number of last-resort antibiotics.
This mechanism was first discovered in E. coli (strain SHP45) from a pig but it was later found by independent researchers in human samples. MCR-1 is the first known polymixin resistance mechanism capable of horizontal gene transfer.
The spread of the plasmid-mediated colistin resistance gene, mcr-1, into carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) clinical isolates poses a significant threat to global health.
Mcr-1 gene is responsible for resistance against the antibiotic, Colistin which is considered as the last mile antibiotic that the human race has currently access to. Colistin belongs to a group of antibiotics called polymixins which are termed “critically important by WHO.
Mcr-1, the gene is found in the plasmid medium, a small DNA molecule outside of the chromosomal DNA and hence the infection can spread in hospitals and the community now.