Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Local self-government in India
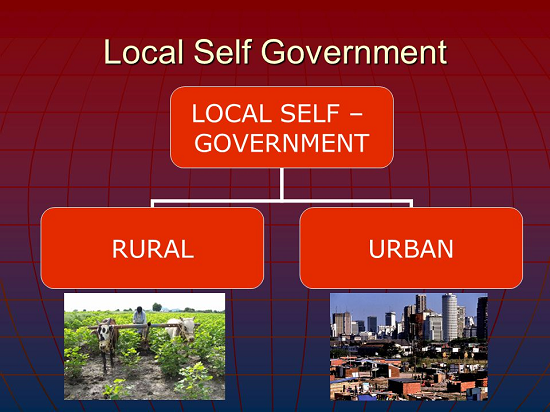
In India local self-government refers to governmental jurisdictions below the level of the state
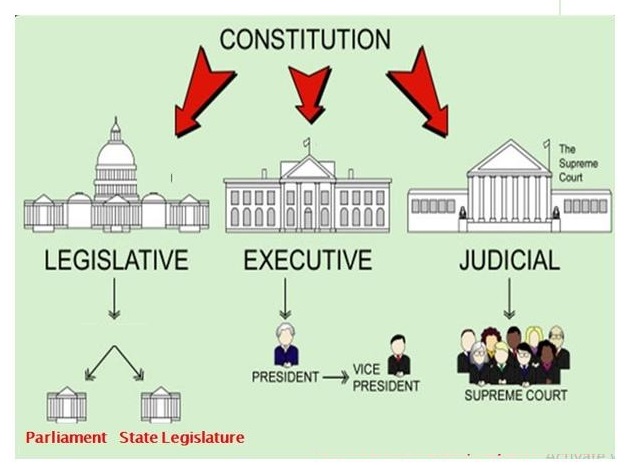
India is a federal republic with three spheres of government: central (union), state and local.
The 73rd and 74th constitutional amendments provide recognition and protection to local governments and in addition to this, each state has its own local government law.
Since 1993, local government in India takes place in two very different forms. Urban localities, covered in the 74th amendment to the Constitution, have Nagar Palika but derive their powers from the individual state governments.
While the powers of rural localities have been formalized under the Panchayati Raj system, under the 73rd amendment to the Constitution.
For the history of traditional local government in India and South Asia, see Panchayati Raj.
As of summer 2017, there are a total of 267,428 local government bodies out of which 262,771 are rural and 4,657 are urban.
Out of the rural local governments, there are 632 are Zila Parishad at the district level, there are 6,672 panchayat Samiti at the block level, and there are 255,466-gram panchayats at the village level.
Panchayati Raj system is a three-tier system with the elected bodies at the village, taluk and district levels.