Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
The Mauryan Empire - Chandragupta and Asoka Governance
The Mauryan empire: Origin, Governance, Wars, Legacy
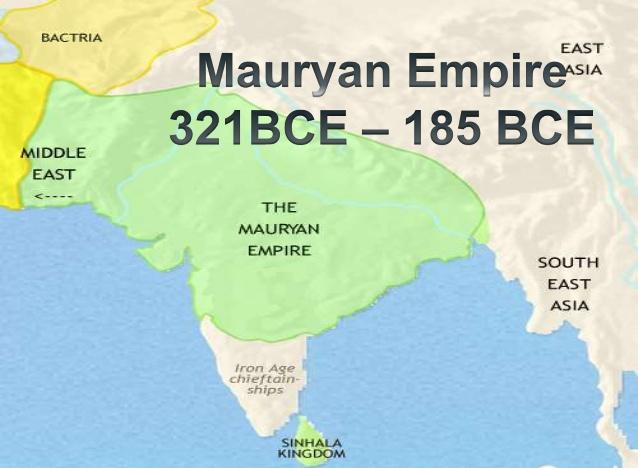
It was one of the greatest empires recorded in India history. The rule of Mauryas lasted from 322 – 185 B.C. where the majority of India was united as a single state by the great founder emperor Chandragupta Maurya. With the help of Kautilya or Chanakya, Chandragupta Maurya laid the foundation of this vast empire.
Chandragupta Maurya (322 – 298 B.C.)
· Chandragupta Maurya was the first ruler who unified the entire country into one political unit, called the Mauryan Empire. He had captured Pataliputra from Dhanananda, who was the last ruler of the Nanda dynasty.
- He didn’t do achieve this feat alone, he was assisted by Kautilya, who was also known as Vishnugupta or Chanakya. Some scholars think that Chanakya was the real architect of this empire.
- After establishing his reign in the Gangetic valley, Chandragupta Maurya marched to the northwest and conquered territories up to the Indus. In the north, he occupied the region north of river Narmada.
- In 305 B.C., he defeated Selukas Niketar, who was controlling the northwestern part of India that was under Greek control.
- A treaty was concluded, under which, Selukas Niketan ceded the territories of Kabul, Kandahar, Herat, Baluchistan – to the Mauryan Empire. He gave his daughter in marriage to the Mauryan Prince.
- Seleucus sent Megasthenes to the Mauryan court as Greek ambassador.
- Greeks called him Sandrocottas.
- He established a vast empire, extending from Afganistan to Assam and from Kashmir to Karnataka(except Kalinga).
- Later in life, Chandragupta embraced Jainism and stepped down from the throne for his son Bindusara to take over. Thereafter he went to Sravana Belgola, in Karnataka along with Jain monks who were led by Bhadrabhagu and starved himself to death.
Asoka the Great (273 – 232 B.C.)
- About his early life, only a few things are known. He served as Governor of Ujjain and also took care of Taxila during his father Bindusara’s reign to help his brother who was facing a revolt.
- He was the first ruler in Indian history who has left his records on engraved stones.
- His inscriptions are found in India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Nepal at 47 places.
- His name is found on only the copies of Minor Rock edict I at 1 place in MP and 3 places in Karnataka.
- The most important event of Asoka’s reign was his war with Kalinga in 261 B.C.about which he has mentioned in the Rock edict XIII. This describes in detail the horrors of war, that deeply disturbed him.
- Under the effect of Kalinga war, Asoka embraced Buddhism by the influence of Buddhist monk, Upagupta.
- The extent of Asoka’s Empire: Ashoka added Kalinga to his territory.


