Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Geo-morphology: Vulcanism & Diastrophism, formation, procedure, landforms, details

Volcanic and Diastrophic forces on the earth's surface and formation of various landforms
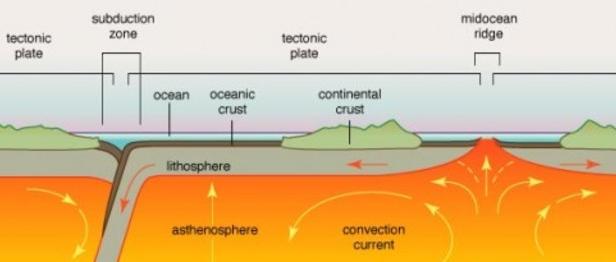
Vulcanism and diastrophism are two endogenic processes of geomorphology. Diastrophism covers the movement of solid (plastic) crust material, as opposed to the movement of molten material which is covered by vulcanism.
These forces derive their energy from changes such as radioactivity, chemical recombination, expansion or contraction or displacement of molten materials which Occurs in the interior of the earth.
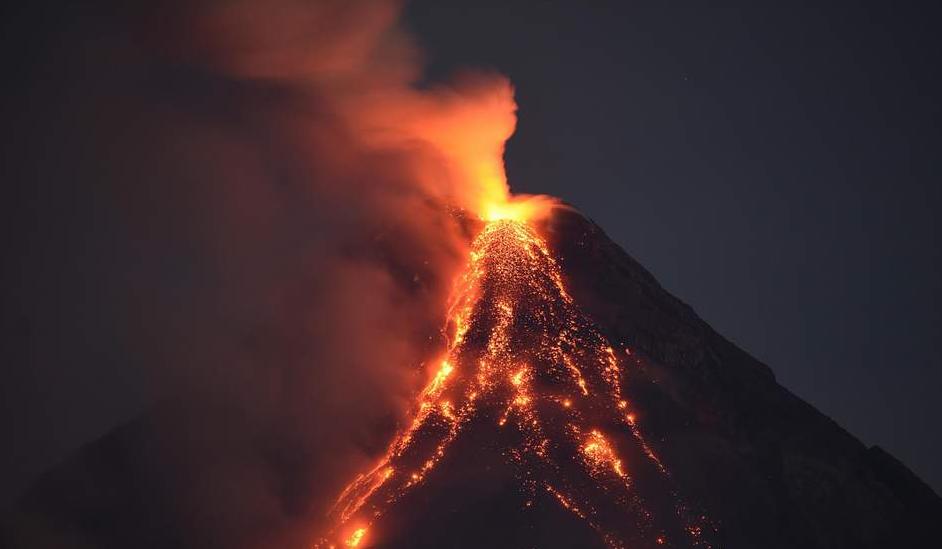
These processes create, modify and continuously affect the landscape of the earth. A volcano is a place where gases, ashes and/or molten rock material - magma/ lava escape to the ground. In this process, molten rock material called magma in asthenosphere find their way to the surface where it is called as lava.
The way a volcano erupts and the materials that make up the magma and lava of a particular volcano have a lot to do with the formation of the volcanic landforms, such as craters, calderas, lava domes, and lava plateaus.
Some of the landforms associated with volcanism are Craters - crater is a bowl-shaped depression at the top of a volcano caused by past volcanic eruptions.
A volcanic crater is relatively small, usually spanning about a half a mile in diameter or less, and can fill with water to form a crater lake. Caldera If a volcanic eruption causes the magma chamber to empty, the volcano can implode, forming a larger depression known as a caldera.
Diastrophic forces operate very slowly and their effects become discernible after thousands and millions of years. These forces are also termed constructive forces, affect large areas of earth and produce meso-level reliefs such as mountains, Plains, Plateaus, lakes, big faults etc.