Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Wind Movement: Coriolis Force, Causes, Rotation of the Earth, Mechanism, Effects
Coriolis Force: Definition, Origin, Mechanism, Effects
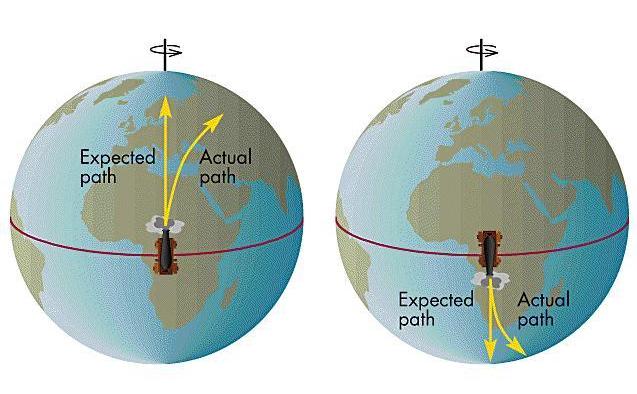
The Coriolis force acts in a direction perpendicular to the rotation axis and to the velocity of the body in the rotating frame and is proportional to the object's speed in the rotating frame.
The Coriolis effect is caused by the rotation of the Earth and the inertia of the mass experiencing the effect. Because the Earth completes only one rotation per day, the Coriolis force is quite small, and its effects generally become noticeable only for motions occurring over large distances and long periods of time, such as large-scale movement of air in the atmosphere or water in the ocean.
Such motions are constrained by the surface of the earth, so only the horizontal component of the Coriolis force is generally important.
The horizontal deflection effect is greater near the poles and smallest at the equator, since the rate of change in the diameter of the circles of latitude when traveling north or south, increases the closer the object is to the poles.
The Coriolis deflection is therefore related to the motion of the object, the motion of the Earth, and the latitude.


