Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Mutation: Definition, Genetic algorithm, testing, and theory
Mutation: Definition, Genetic algorithm, testing, and theory
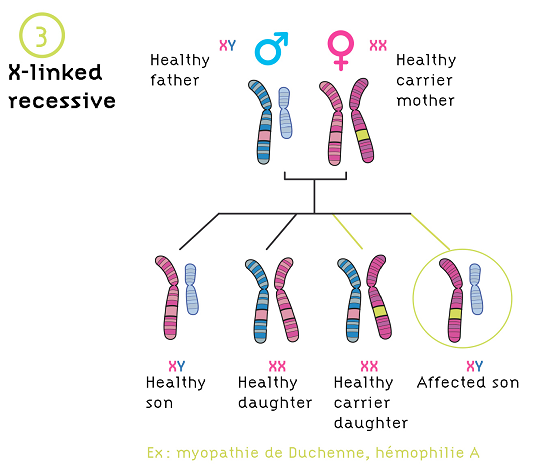
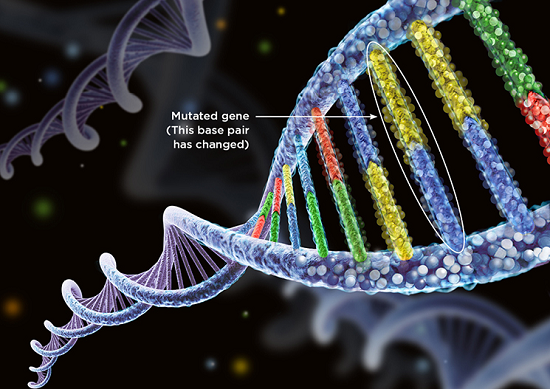
Mutation is a substitution of a genetic sequence. Mutations incorporate shifts as inadequate as the replacement of a particular DNA structure block, or nucleotide base, with different nucleotide base.
When massive changes can alter many genes on a chromosome. Adjacent by replacements, changes can also be caused by insertions, deletions, or duplications of DNA sequences that is called as a mutation.
Any changes are inherited because all are carried down to children from a parent providing a modification within the germline, suggesting by an embryo or sperm cell transmitting the mutation.
There are also nonhereditary modifications that occur in cells outside of the germline, which is called somatic mutations.
Mutations can be injected due to errors caused during DNA replication or due to susceptibility to mutagens, which are biochemical and environmental factors that can inject modifications in the DNA series, before-mentioned as UV light.
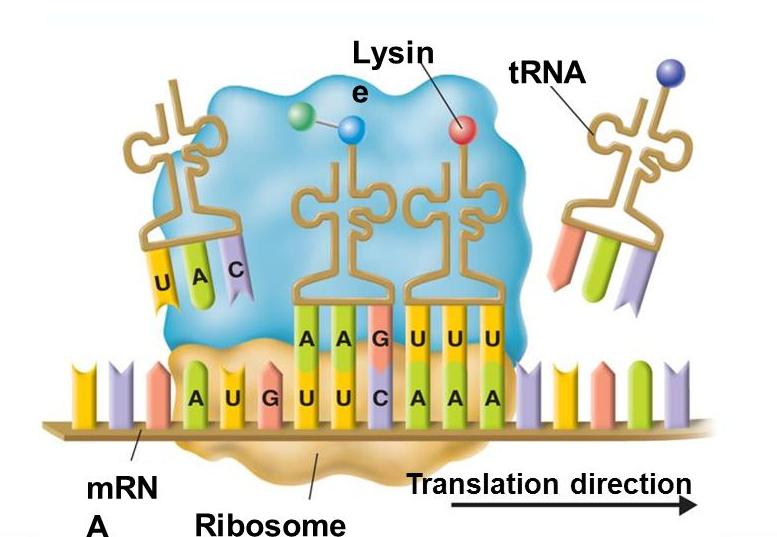
Any changes do not result in a mutation in the amino acid subsequence of the encoded protein and can be called silent mutations. Different mutations occur in unusual protein products.
Mutations can begin different alleles within a group of animals and enhance the population's genetic modification.