Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Definition Of Democratic Constitution And Need Of Constitution

Definition Of Democratic Constitution And The role of a democratic country with a well-established constitution
A Constitution is a set of fundamental principles by which a country is Governed.
A democratic country is where the sovereign power to rest with people, to elect representatives who make decisions on behalf of them.
The role of a democratic country with a well-established constitution
To protect the interests of minorities and underprivileged eg: secularism, untouchability
To protect the Fundamental rights of the people eg: right to vote
To provide the guiding principles to the Government eg: DPSP
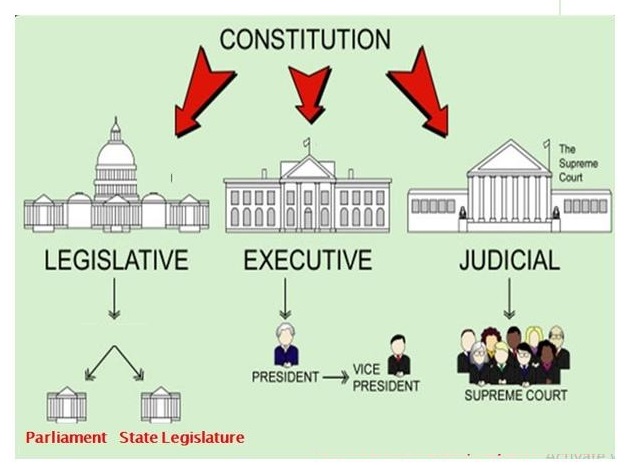
Separation and balance of powers between the organs of the Government eg: executive, judiciary and legislative
To keep reasonable restrictions on the elected representatives eg: judicial review
To protect the ideals and culture of the country eg: right to protect religion
To protect the unity and integrity of the nation eg: India is a union of states
To establish rule of law eg: no one is above the law
To protect the independence of the Institutions to ensure proper functioning of democracy eg: election commission, upsc
To provide social, economic and political justice to all its citizens eg: right to contest in the election despite caste, creed, and religion
Constitution safeguards the liberties of its citizens in a democratic country.