Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Constitution: Introduction to the Indian Constitution

Constitution: Introduction to the Indian Constitution applicable from 26 Jan 1950, Power And Law
The Constitution of India is the world's longest written constitution with 395 articles and 8 schedules. It contains the good points constitution of many countries in the world.
It was passed by 'The Constituent Assembly' on November 26, 1949, and is fully applicable from 26 Jan 1950. The Constituent Assembly had been elected for undivided India and held its first meeting on 9th Dec. 1946,
on the 14th August 1947, was reunited in the form of The Sovereign Constituent Assembly for India's dominance. In regard to its composition, the members were elected by indirect election by the members of The Provisional Legislative Assemblies (lower house only).284 out of 299 members of the Assembly were present at the time of signing.
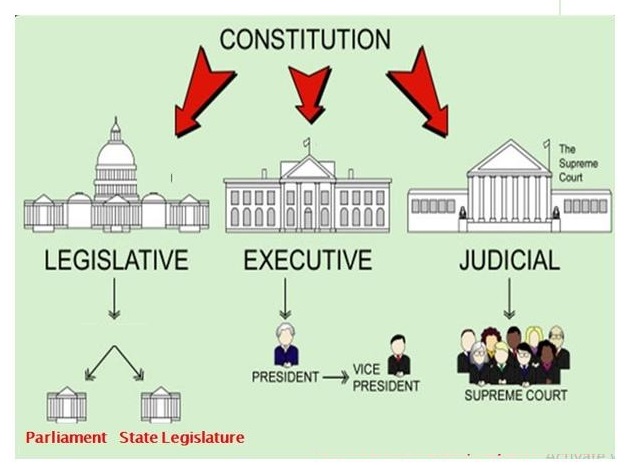
The constitution of India attracts extensively from Western legal traditions in its outline of the principles of liberal democracy. It follows a British parliamentary pattern with a lower and upper house.
India is a federal system in which remaining powers of law reside with the central government, similar to that in Canada. The constitution provides detailed lists dividing up powers between central and state governments as in Australia, and it describes a set of Directive Principles of State Policy as does the Irish constitution.