Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Cell Division: definition, types of cell division, mechanism
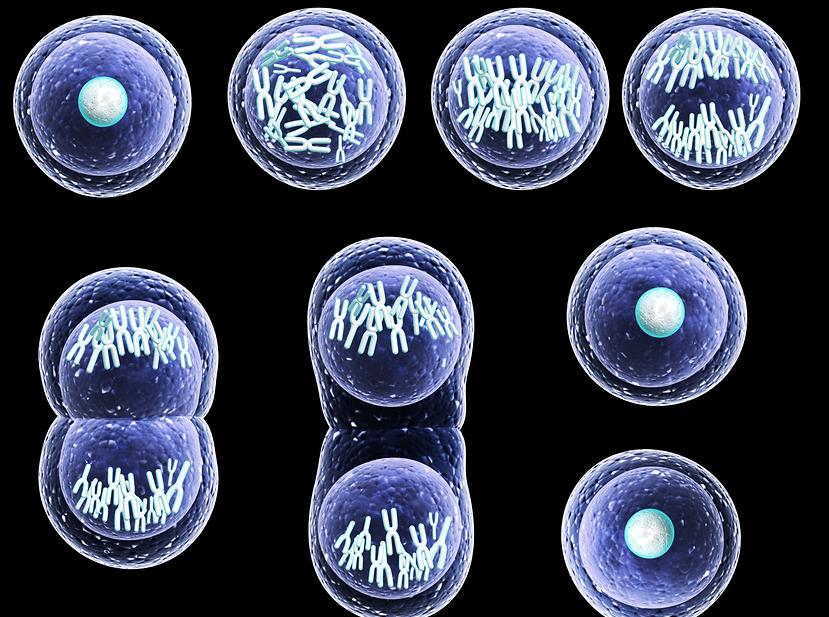
Cell Division- Mitosis, Meiosis, and Binary Fusion
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more cells called daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle. All cells reproduce by dividing into two, with each parental cell giving rise to two daughter cells every time they divide.
These newly formed daughter cells could themselves divide and grow, giving rise to a new cell population that is formed by the division and growth of a single parental cell and its descendant.
In other words, such cycles of growth and division allow a single cell to form a structure consisting of millions of cells.
There are two distinct types of cell division out of which the first one is vegetative division, wherein each daughter cell duplicates the parent cell called mitosis. The second one is meiosis, which divides into four haploid daughter cells.
Mitosis: The process cells use to make exact replicas of themselves. Mitosis occurs throughout the majority of the body’s cells, including skin, eyes, hair, and muscle cells.
Meiosis: The second type of cell division is called meiosis. This division produces sperm or egg cells, not identical daughter cells as in mitosis.
Binary Fission: Single-celled organisms like bacteria replicate themselves for reproduction.


