Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Biology: Cilia and Flagella Features, Structure, Functions, Types, Role
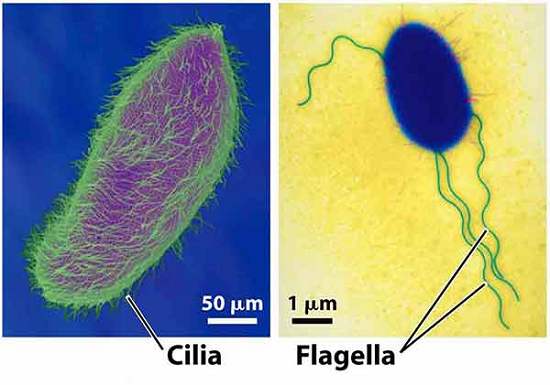
Biology: Definition of Cilia and Flagella, Structure, Function, and their types
Cilia and Flagella are hair-like outgrowths of the cell membrane. Celia is small structures that work like oars, causing movement of the cell or surrounding fluid. Flagella are the comparatively long-term and responsible for cell movement.
The prokaryotic bacteria also possess flagella but they are structurally different from the eukaryotic flagella.
The electron microscopic studies of a cilium or that flagellum show that they are covered with the plasma membrane. Their core called the axoneme, possesses a number of microtubules running parallel to the long axis.
The axoneme usually has nine parts of doublets of radially arranged peripheral microtubules, and a pair of central-located microtubules. Such a system of axonemal microtubules is referred to as the 9+2 array.
The central tubules are attached to bridges and are surrounded by a central sheath, which is connected by a radial spoke to one of the tubules of each peripheral doublets. Thus, there are nine radial spokes. Peripheral double are also connected by linkers. Both the cilium and the flagellum have emerged from the structure like the centriole called the basal bodies.


