Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Gel electrophoresis technique: Definition, process, steps, purpose, facts
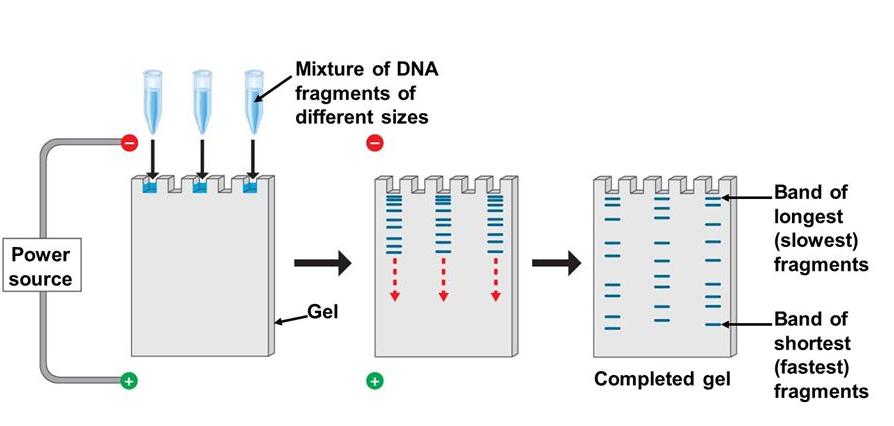
What is gel electrophoresis technique and what it is used for? Definition, Procedure, and Facts
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory method used to separate mixtures of DNA, RNA, or proteins according to molecular size.
In gel electrophoresis, the molecules to be isolated are forced by an electrical field through a gel that comprises small pores.
The molecules move by the holes in the gel at a speed that is inversely associated to their lengths. This indicates that a small DNA molecule will travel a greater distance through the gel than will a larger DNA molecule.
gel electrophoresis involves an electrical field; in particular,
this field is used such that one point of the gel has a positive charge and the other point has a negative charge.
DNA and RNA are negatively charged molecules, they will be attracted toward the positively charged end of the gel.
Proteins, however, are not negatively charged thus, when researchers want to separate proteins using gel electrophoresis, they must first mix the proteins with a detergent called sodium dodecyl sulfate.
This treatment makes the proteins unfold into a linear shape and coats them with a negative charge, which allows them to migrate toward the positive end of the gel and be separated.
Finally, protein molecules have been isolated using gel electrophoresis, bands designing molecules of different sizes can be identified.


