Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Deoxyribonucliec Acid(DNA): Introduction, Discovery, Chemical Structure, Significance
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA): Definition, Structure, Discovery, Functions
Definition:- DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. It is located in the nuclei of cells, which make up the body. Consequently, DNA can be considered as one of the building blocks of the body. These instructions are found inside every cell and are passed down from parents to their children.
Discovery:- DNA was first recognized by a German biochemist named Frederich Miescher in 1869. But for many years, researchers did not realize the significance of this molecule.
It was not until 1953 that James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins, and Rosalind Franklin figured out the structure of DNA a double helix which they realized could carry biological information.
Watson, Crick, and Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1962.
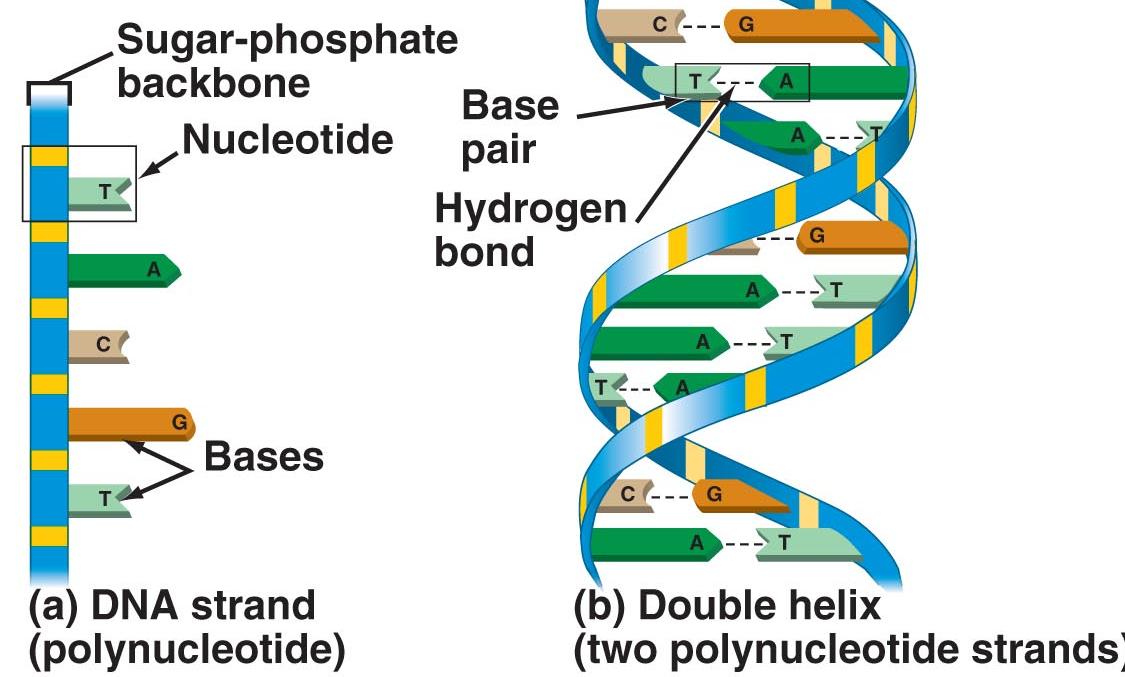
Structure:- DNA is made up of molecules called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar group, and a nitrogen base. The four types of nitrogen bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The order of these bases is what determines DNA'S genetic code. Human DNA has around 3 billion bases, and more than 99% of those bases are the same in all people.


