Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Vitamins and Minerals: types, works, and functionality
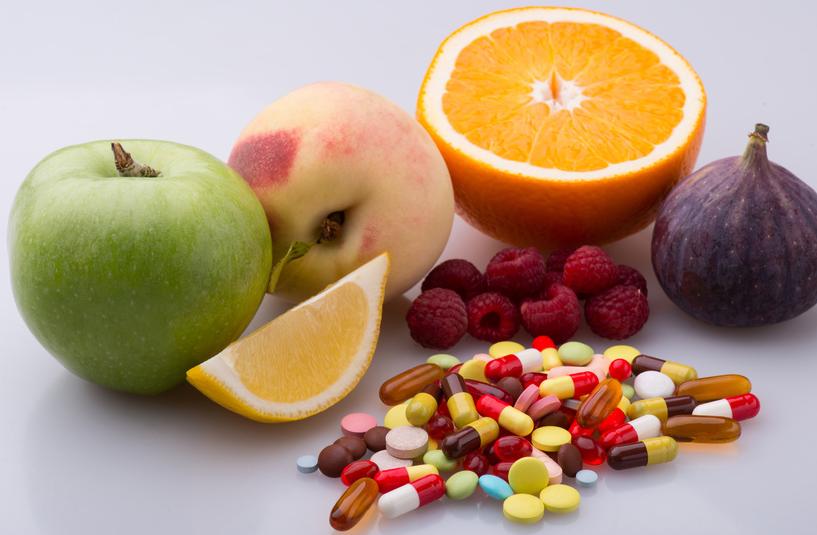

Types and usefulness of Vitamins & Minerals
Vitamins help in the body growth and work the way it should. There are 13 vitamins—vitamins C, A, D, E, K, and the B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, B6, B12, and folate). Most of the vitamins cannot be synthesized in our body but plants can synthesize almost all of them, so they are considered as essential food factors.
There are two types of vitamins: fat soluble and water soluble.
Fat-soluble vitamins are happy to stay stored in your body for awhile — some stay for a few days, some for up to 6 months! Then, when it's time for them to be used, special carriers in your body take them to where they're needed. Vitamins A, D, E, and K are all fat-soluble vitamins.
Water-soluble vitamins are different. When you eat foods that have water-soluble vitamins, the vitamins don't get stored as much in your body. Instead, they travel through your bloodstream. Whatever your body doesn't use comes out when you urinate.
Minerals also help your body function. Some minerals, like iodine and fluoride, are only needed in very small quantities. Others, such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, are needed in larger amounts. As with vitamins, if you eat a varied diet, you will probably get enough of most minerals. They are inorganic nutrients that also play a key role in ensuring the health.