Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Animal Tissues – Definition of tissue, Epithelium tissue and Connective tissue
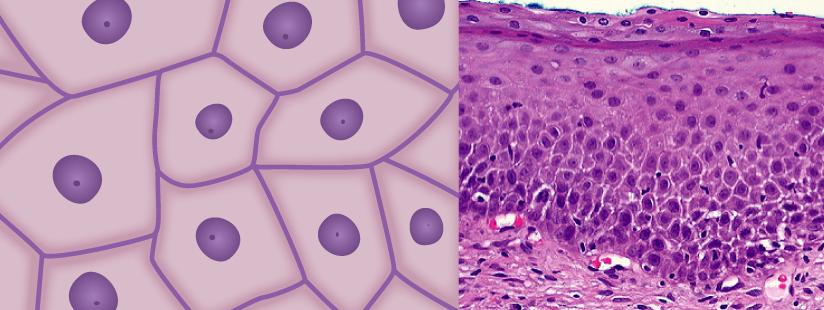
Animal Tissues, definition, classification, and functions
A group of cells similar in structure, function, and origin is called tissues. In animals, the structure of a tissue depends on its function. An animal body is made of four different types of tissues. They have been classified based on the type of cell, function, and location in the body.
Epithelial Tissue:- All layers and organs in the body are lined by a group of tissues called epithelial tissues which are commonly referred to as epithelium. They cover the surface of all internal as well as external organs. Epithelial tissue is highly permeable. it plays a significant role in the exchange of substances across the cells and helps in maintaining the osmoregulation. Depending on the number of layers of cells it is composed of, epithelium has been divided into simple epithelium and compound epithelium. The main functions of epithelial tissue are protection, secretion, absorption, and sensation.
Connective tissue:- As their name suggests, they connect and support the different tissues, organs, and parts of the body. Among the animal tissues, connective tissues are the most abundant ones in the body. The connective tissue cells are freely arranged in a matrix and are widely distributed in the body. Different types of connective tissues include areolar tissue, adipose tissue (fat), blood, bone, and cartilage. Except for blood, all other cells secrete collagen (elastin) which offers elasticity and flexibility to the tissues


