Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Radioactivity: definition, alpha, beta and gamma rays, reactions
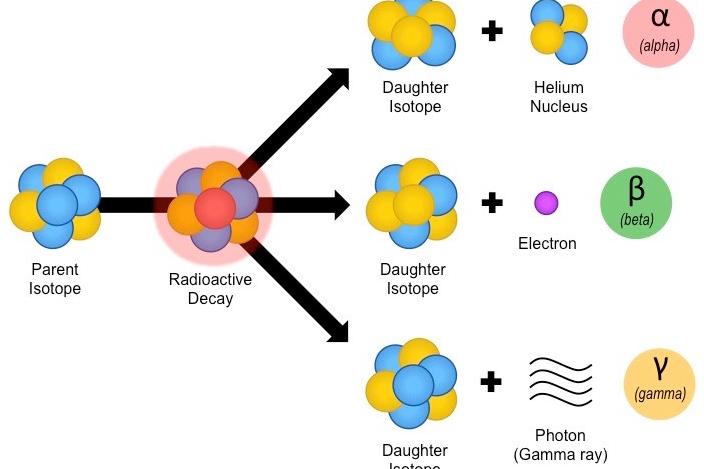
Emission of alpha, beta and gamma rays, and radioactivity
The distance between the two protons in the large nuclei decreases so much that the repulsive force, due to their same electrical charge in the protons, is greater than the force that takes place between them, the nuclear force. goes.
It has been found that the number of protons in the nucleus is 83 or more, they are temporary. To achieve stability, these nuclei automatically begin to emit alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (y) rays.
Such nuclei, which are in atoms, are called radioactive elements, and the phenomena of the emissions of the above-mentioned rays are called radioactivity.
The alpha (α) rays are actually made up of positive helium nuclei and beta(β) rays are electrons with only fast moving passages. The gamma (y) rays are made of chargeless photon particles.
When alpha rays or beta rays emitted from a nucleus, then the nucleus turns into a new element of the nucleus. If this nucleus is in a state of excitement, then it stimulates its stimulating energy into gamma rays and comes into its original state. Thus gamma rays are emitted after alpha or beta rays.
Converting a radioactive element into another element is called a Transmutation. The half-life of the radioactive element is fixed. Half age of different elements is found between 10-7 seconds.
