Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Endocrine System, bodily functions, endocrine glands, hormonal regulation
Definition of the Endocrine system and function of the endocrine glands-
The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones, chemical substances produced in the body that regulate the activity of cells or organs. These hormones regulate the body's growth, metabolism (the physical and chemical processes of the body), and sexual development and function. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and may affect one or several organs throughout the body.
A gland is a group of cells that produces and secrets or gives off, chemicals. A gland selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body.
Some types of glands release their secretions in specific areas. For instance, exocrine (pronounced: EK-suh-Krin) glands, such as the sweat and salivary glands, release secretions in the skin or inside the mouth. Endocrine glands, on the other hand, release more than 20 major hormones directly into the bloodstream where they can be transported to cells in other parts of the body.
The endocrine system is regulated by feedback in much the same way that a thermostat regulates the temperature in a room.
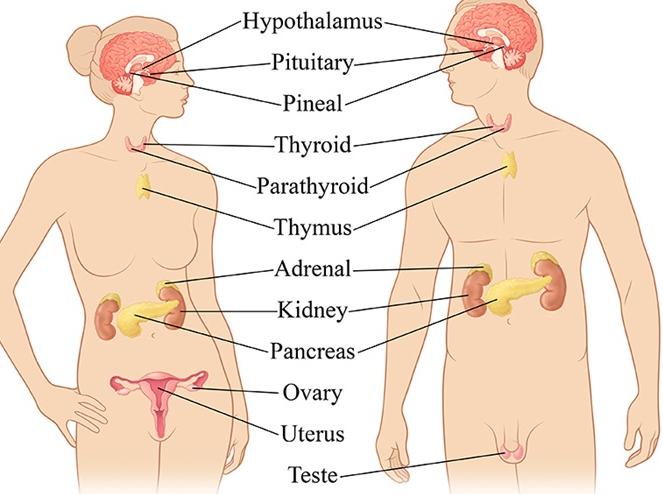
The major glands that make up the human endocrine system include the:
- hypothalamus
- pituitary gland
- thyroid
- parathyroids
- adrenal glands
- pineal body
- reproductive glands (which include the ovaries and testes)
- pancreas