Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Biogeography Zones Features, Plants and Animals of India
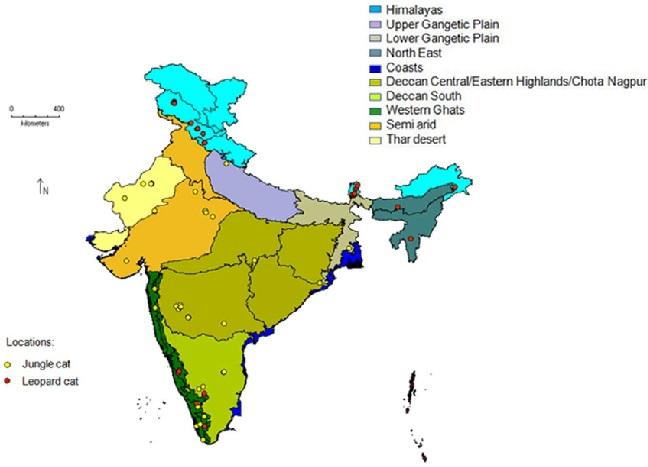
Biogeography Zone of India Features, Plants and, Animals
The Biogeography deals with the geographical distribution of plants and animals. There are 10 bio-geographical Zones in India.
The Himalayan ranges immediately north of the Great Himalayan range are called the Trans- Himalayas.
The Himalayas consist of the youngest and loftiest mountain chains in the world.
Adjoining the desert are the semi-arid areas, a transitional zone between the desert and the denser forests of the Western Ghats. The natural vegetation is thorn forest.
The mountains along the west coast of peninsular India are the Western Ghats, which constitute one of the unique biological regions of the world.
This region consists of parts of Rajasthan, Kutch, Delhi and parts of Gujarat. The climate is characterised by very hot and dry summer and cold winter. Rainfall is less than 70 cm. The plants are mostly xerophytic.
Beyond the Ghats is Deccan Plateau, a semi-arid region lying in the rain shadow of the Western Ghats. This is the largest unit of the Peninsular Plateau of India.
In the North is the Gangetic plain extending up to the Himalayan foothills. This is the largest unit of the Great Plain of India. Ganga is the main river after whose name this plain is named.
India has a coastline extending over 7,516. 4 km. The Indian coasts vary in their characteristics and structures.